SPINAL CORD INJURY REHAB
Spinal Cord Injuries (SCI) can be defined as a traumatic or non-traumatic event that leads to neural damage that influences motor-, sensory – and respiratory function, as well as bladder -, bowel – and sexual function. The neurological interruption also affects the individual’s blood pressure, skin integrity and ability to regulate temperature.
SCIs don’t only have an impact on the individuals’ physical – and emotional well-being, but it also has a considerable impact on families, communities and healthcare systems worldwide. Literature indicates the peak age between 12 and 30 years, with an average life span as 30.2 years following injury.
SCI, most commonly, results in paraplegia or tetraplegia. Paraplegia is the loss in motor and/ or sensory function in the lower limbs (LLs) and trunk. While tetraplegia includes the upper limbs (ULs) to the motor and/ or sensory loss of the LLs and trunk.
Physiotherapy management
The acute management and rehabilitation of SCI depend on the level and type of injury to the spinal cord. Individuals with a SCI often require initial treatment in an intensive care unit with the rehabilitation process typically starting in the acute care setting, followed by extended treatment in a specialized Spinal Injury Unit.
The management of an individual with SCI is complex and lifelong requiring a multidisciplinary approach. A functional, goal-oriented, interdisciplinary, rehabilitation program should enable the individual with a spinal cord injury to live as full and independent a life as possible. Physiotherapy, occupational therapy, speech and language therapy, rehabilitation nurses, social workers, psychologists and other health work as a team to decide on goals with the individual and develop a plan of discharge that is appropriate for the individuals level of injury and circumstances.
Five key steps in the management of individuals with SCI are;
- Assessing impairments, activity limitations and participation restrictions
- Setting goals relevant to activity limitations and participation restrictions
- Identifying key impairments that are limiting achievement of goals
- Identifying and administering physiotherapy treatments (strengthening, joint mobility, motor skill development, cardiovascular fitness, respiratory functioning, pain managing)
- Measuring the outcome of treatments
The management of individuals with a SCI can be divided into 3 Phases;
- Acute,
- Sub-acute (Rehabilitation), and
- Chronic (Long Term).
During the acute and subacute phases of treatment, rehabilitation strategies focus more on prevention of secondary complications, promoting neuro recovery, addressing underlying impairments and maximizing function. In the chronic phase, compensatory or assistive approaches are often used
We work mainly on
Objective
- Bed mobility
- Sitting balance training
- Transfers training
- wheelchair mobility skills
- Standing balance
- Treadmill walking
- Waling training with orthotics
Click on below for more videos
PARAPLEGIC REHAB
QUADRIPLEGIC REHAB
PARAPLEGIC CASE STUDIES
Why Aquatic therapy? What is the benefit? Who can Benefit from it?
Article by: Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao (PT) MPT neuro PT , C/NDT (USA), Aquatic therapy (Kliniken Valens Switzerland)

Physical Therapy is a constantly evolving field. There are many types and methods are adding as adjunct traditional physical therapy. Most of these therapies are performed on the land. There are multiple forces are always acting on our body in any given instant. the forces can be internal or external forces. Our muscles and body mechanics always have work against or with these forces to move. There is always one force acts on everything including our body is the constant force of gravity. Gravity acts on everything all the time. We move against or towards the force of gravity. We try to stabilize our body against the force of gravity. Amount of muscles work and effort depends on what is the body alignment with respect to gravity.
Benefit from Aqua therapy
- Reduce weight bearing on lower limb – helps in partial weight bearing walking gradation
- Assist in stability and balance
- Makes Movement easy and assisted
- Gives resistance to movements,
- Easy to change the grading of resistance
- High intensity training with less fatigue and injury to muscles and ligaments
- Less stress on ligaments in closed chain positions
- Helps in general body relaxation – stress management
- Joint mobilization hip, knee, ankle, shoulder & elbow with less pain even with high intensity mobilization
- Improving range of motion
- Spinal joint mobilization
- Muscle relaxation
- Non weight bearing walking – deep water walking with floats
- Strength training
- Endurance training
- Agility & plyometrics training
- Balance training
- Reduce tone/spasticity /rigidity/ tightness
- Graded loading on labrum/ capsule and ligaments of joints
- Coordination training
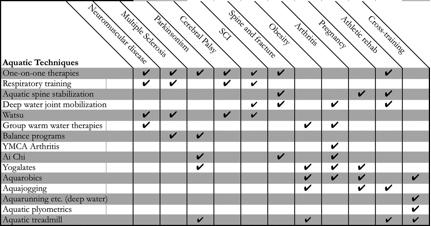
Whom to contact for aquatic therapy?
Ans -Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao, 9822623701. schoolneurorehab@gmail.com
GB school of neuro rehab and aquatic therapy, Bungalow no 1. Gajanan Housing society Model colony Shivajinagar Pune 16. Direction and Maps
WHAT IS AQUATIC THERAPY?
There are multiple methods are developed to reduce the effect of gravity and using buoyancy.
- Body weight supported treadmill training
- Robotic locomat
- Space walk training simulator
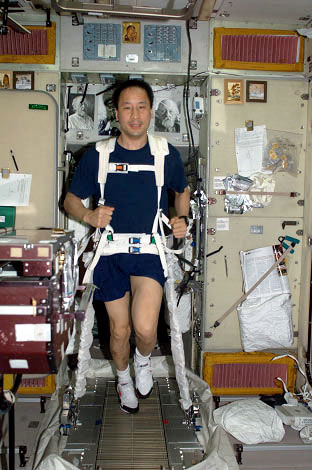
- Aqua treadmill
- Aqua gym
Aqua cycling
All these method of training have advantage and disadvantages.
- Most of these are targeted at only walking training (alter G, body weight supported treadmill training, aqua treadmill), cycling (aqua cycling) and strengthening ( aqua gym) individual muscles.
- Body weight supported treadmill training is not very comfortable for patient (harness and un- weighing). it requires lots of effort by therapist to put legs forward during walking.

- Aqua treadmill : we can do limited exercises of walking forward, backward, sideways or running only.
There is need of therapy where there is more flexibility of selection of therapeutic exercises and activities. So Aquatic therapy play a major role is in this.
What is aquatic therapy?
Aquatic therapy refers to treatments and exercises performed in water for relaxation, fitness, physical rehabilitation, and other therapeutic benefit. Typically a qualified aquatic therapist gives constant attendance to a person receiving treatment in a heated therapy pool. Aquatic therapy techniques include Ai Chi, Aqua Running, Bad Ragaz Ring Method, Burdenko Method, Halliwick, Watsu, and other aquatic bodywork forms. Therapeutic applications include neurological disorders, spine pain, musculoskeletal pain, postoperative orthopedic rehabilitation, pediatric disabilities, and pressure ulcers.
Aquatic therapy refers to water-based treatments or exercises of therapeutic intent, in particular for relaxation, fitness, andphysical rehabilitation. Treatments and exercises are performed while floating, partially submerged, or fully submerged in water. Many aquatic therapy procedures require constant attendance by a trained therapist, and are performed in a specialized temperature-controlled pool. Rehabilitation commonly focuses on improving the physical function associated with illness, injury, or disability.[1][2]
Aquatic therapy encompasses a broad set of approaches and techniques, including aquatic exercise, physical therapy,aquatic bodywork, and other movement-based therapy in water (hydrokinesiotherapy). Treatment may be passive, involving a therapist or giver and a patient or receiver, or active, involving self-generated body positions, movement, or exercise. Examples include Halliwick Aquatic Therapy, Bad Ragaz Ring Method, Watsu, and Ai chi.[1]
For orthopedic rehabilitation, aquatic therapy is considered to be synonymous with therapeutic aquatic exercise, aqua therapy, aquatic rehabilitation, water therapy, and pool therapy. Aquatic therapy can support restoration of function for many areas of orthopedics, including sports medicine, work conditioning, joint arthroplasty, and back rehabilitation programs. A strong aquatic component is especially beneficial for therapy programs where limited or non-weight bearing is desirable and where normal functioning is limited by inflammation, pain, guarding, muscle spasm, and limited range of motion (ROM). Water provides a controllable environment for reeducation of weak muscles and skill development for neurological and neuromuscular impairment, acute orthopedic or neuromuscular injury, rheumatological disease, or recovery from recent surgery.[3]:1
Various properties of water contribute to therapeutic effects, including the ability to use water for resistance in place of gravity or weights; thermal stability that permits maintenance of near-constant temperature; hydrostatic pressure that supports and stabilizes, and that influences heart and lung function; buoyancy that permits floatation and reduces the effects of gravity; and turbulence and wave propagation that allow gentle manipulation and movement.[4]
Techniques
Techniques for aquatic therapy include the following:
- Halliwick Concept: The Halliwick Concept, originally developed by fluid mechanics engineer James McMillan in the late 1940s and 1950s at the Halliwick School for Girls with Disabilities in London, focuses on biophysical principles of motor control in water, in particular developing sense of balance (equilibrioception) and core stability. The Halliwick Ten-Point-Program implements the concept in a progressive program of mental adjustment, disengagement, and development of motor control, with an emphasis on rotational control, and applies the program to teach physically disabled people balance control, swimming, and independence.
- Water Specific Therapy, WST: Halliwick Aquatic Therapy (also known as Water Specific Therapy, WST), implements the concept in patient-specific aquatic therapy. This concept is very good for rehabilitation of neurological and orthopedic impairment. This is tailer made approach for individual needs and problems. In this you can on the motor control as whole body & its movements in all direction and individual motor muscle control. You can do task specific training i.e. sit to stand, balance in walking, one leg stance, walking and balance again resistance of water, coordination exercises, core strengthening in task, postural control and motor control in various task.
- Bad Ragaz Ring Method: The Bad Ragaz Ring Method (BRRM) focuses on rehabilitation of neuromuscular function using patterns of therapist-assisted exercise performed while the patient lies horizontal in water, with support provided by rings or floats around the neck, arms, pelvis, and knees. BRRM is an aquatic version of Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) developed by physiotherapists at Bad Ragaz, Switzerland, as a synthesis of aquatic exercises designed by a German physician in the 1930s and land-based PNF developed by American physiotherapists in the 1950s and 1960s.
- https://youtu.be/A0-DGEP4F1U
- Ai Chi: Ai Chi, developed in 1993 by Jun Konno, uses diaphragmatic breathing and active progressive resistance training in water to relax and strengthen the body, based on elements of qigong and Tai chi chuan.
- Aqua running: Aqua running (Deep Water Running or Aquajogging) is a form of cardiovascular conditioning, involving running or jogging in water, useful for injured athletes and those who desire a low-impact aerobic workout. Aqua running is performed in deep water using a floatation device (vest or belt) to support the head above water.
- Watsu: Watsu is a form of aquatic bodywork, originally developed in the early 1980s by Harold Dull at Harbin Hot Springs, California, in which an aquatic therapist continuously supports and guides the person receiving treatment through a series of flowing movements and stretches that induce deep relaxation and provide therapeutic benefit. In the late 1980s and early 1990s physiotherapists began to use Watsu for a wide range of orthopedic and neurologic conditions, and to adapt the techniques for use with injury and disability.
Healing Dance
Aqua aerobics:
Top 6 reasons to use aqua aerobics for exercise:
1)Heart health. heart rate will be about 13 percent more slower – about 17 fewer heart beats a minute.
2)The enjoyment: If a workout is fun, I’m more likely to keep doing it.
3)The variety.
4)Stress relief.
5)Low impact.
6) Resistance of water
Benefit from Aqua therapy
- Reduce weight bearing on lower limb – helps in partial weight bearing walking gradation
- Assist in stability and balance
- Makes Movement easy and assisted
- Gives resistance to movements,
- Easy to change the grading of resistance
- High intensity training with less fatigue and injury to muscles and ligaments
- Less stress on ligaments in closed chain positions
- Helps in general body relaxation – stress management
- Joint mobilization hip, knee, ankle, shoulder & elbow with less pain even with high intensity mobilization
- Improving range of motion
- Spinal joint mobilization
- Muscle relaxation
- Non weight bearing wallking – deep water walking with floats
- Strength training
- Endurance training
- Agility & plyometrics training
- Balance training
- Reduce tone/spasticity /rigidity/ tightness
- Graded loading on labrum/ capsule and ligaments of joints
- Coordination training

Who can benefit from Aqua therapy
A. Normal population for fitness and aerobic conditioning, weight loss
B. Orthopedic conditions
1)OA knee
2)Arthroplasty ACL,MCL repairs
3)Knee ligament injuries – conservative/ post op
4)Rheumatoid arthritis/ Ankylosing spondylitis/ Poly arthritis
5)Spine – conservative/ post operative, Low back pain
6) Fractures – conservative/post-op
C. Neurological conditions
1. Stroke rehab, Hemiplegic- upper limb, lower limb and trunk control training, and strengthening, balance and gait training
2. Paraplegic and quadriplegic – upper limb, lower limb and trunk control training and strengthening, balance and gait training
3. Balance disorders, Parkinson, Ataxia – strengthening, coordination, balance and gait training
4. Peripheral nerve injury and polyneuropathy -strengthening and gait training
5. Traumatic brain injury
D. Pedriatics – Cerebral palsy, DMD, Spina bifida, ataxia, developmental delay -strengthening, coordination, balance and gait training
What are the contraindication?
 Frequently Asked questions about Aquatic therapy ?
Frequently Asked questions about Aquatic therapy ?
Q: Is it necessary to know how to swim for aquatic therapy?
A: It is not necessary to know how to swim, during therapy you will be supported by your therapist or floats.
Q: Can patients without bladder control/ with a catheter participate in aquatic therapy?
A: Patients without bladder control must empty their bladder before aquatic therapy session. In order to participate, patients using a catheter must obtain prior permission from their physician. During therapy, the catheter must be blocked. Due to risk of infection, some public pools might not permit patients with a catheter to enter the pool.
Q: Can patients with bedsore/ open wounds receive aquatic therapy?
A: Yes, patients with bedsore/ open wounds can participate in aquatic therapy after the application of a wet dressing (specialized dressing which prevents water going into the wound). Permission from your physician or surgeon is required before coming for therapy. Risk – there are chances of cross infection and delayed wound healing in some cases if proper precaution is not followed.
Q: Do I need to wear a swimming costume or can I come in regular shorts?
A: Everyone who enters the pool is required to wear a swimming costume. Men shorts and T shirt, Women can use short length or full body costumes. Women or men with long hair are required to wear swimming cap during pool sessions. (It is advised to cover body in order to prevent suntan)
Q: How many sessions do I need to take?
A: There is no right answer to this question. It depends on multiple factors such as type/stage/progression of disease, severity/level of injury, neuroplasticity and learning ability of patient, compliance to therapy, training intensity and frequency of therapy.
10- 15 sessions is recommended in order to evaluate the rate of change and the effect/intensity of therapy. Depending on the results, more sessions may be necessary.
Q: Will aquatic therapy benefit me?
A: Aquatic therapy is one of the modalities of physiotherapy, if you need/are referred to physiotherapy then aquatic therapy will be beneficial as well. Compared to physiotherapy on land, it is easier to move in the water and exercises in water are more fun. You will be assessed on land first to find your impairment, activity and participation restriction. Based on the assessment your therapist will decide if you need aquatic therapy or not. Most of the time a combination of land and aquatic based exercises are beneficial for patients for strengthening, postural/trunk control, balance and gait training.
Q: Can a patient with cardiovascular diseases have aquatic therapy?
A: Cardiovascular disease is not a contraindication but a precaution. Patients with poor cardiovascular capacity, lower ejection fraction, under active/unstable angina should not attend aquatic therapy. When a body is immersed in water changes in blood pressure occur, patients with unstable hypertension of hypotension should to be monitored.
Q: Will I be taught/allowed to do exercises on my own in the pool during/after my aquatic therapy session?
A: Yes, after receiving appropriate training from your aquatic therapist and you are safe to perform exercises by yourself. Make sure that a life guard is on duty and aware of you when exercising alone.
Q: How should I prepare myself for aquatic therapy?
A: Please note the following:
- Before aquatic therapy do not eat heavy food, light food or snacks are advised.
After a long session you might feel tired and hungry, therefore it is advised to bring a snack. - Keep well hydrated: Drink water before/during and after therapy.
- Empty bladder and bowel before therapy.
- Cover wounds with wet dressing before therapy.
- Take bath/shower before entering the pool.
- Check physical fitness and cardio vascular capacity, ability to tolerate exercises in water.
- It is advised to observe other patients’ treatment session to get an overall idea about the therapy in water.
- Bring moisturizer for use after pool session. Do not apply moisturizer before therapy otherwise it will be difficult for the therapist to maintain grip.
- Bring essential showering toiletries and a spare set of clothes (if necessary bring a person/aid for assistance before and after session).
Q: Are there any changes that need to be observed/reported after completing the session?
A: Please report the following after the session:
- How was the therapy experience?
- How did you feel during and post session?
- Did you notice any positive changes after the session?
For example: increased range of motion, strength, endurance, posture and movement - Did you notice any change in your functional ability, level of assistance or independence?
- Presence of any adverse reactions to water or worsening of your present symptoms?
- These issues may come up during the session as well, please report them to your therapist.
- Are you getting any muscle cramps or delayed onset of muscle soreness? If so, please report to your therapist. He/she will advise you on what to do about it.
Whom to contact for aquatic therapy?
Ans -Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao, 9822623701. schoolneurorehab@gmail.com
GB school of neuro rehab and aquatic therapy, Bungalow no 1. Gajanan Housing society Model colony Shivajinagar Pune 16. Direction and Maps
WORKSHOP ON 2D & 3D GAIT ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT Of GAIT DEVIATIONS
Author of article:
DR. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT), PhD Scholor, MPTH NEURO, Certified Adult NDT therapist. HOD Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation Dept in Sancheti Hospital Shivajinagar Pune. Associate Professor & HOD PT in Neuro Rehabilitation DEPT at Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy, Shivajinagar Pune
Sancheti college of physiotherapy is organizing
A WORKSHOP ON
2D & 3D GAIT ANALYSIS AND MANAGEMENT Of GAIT DEVIATIONS
On 20th and 21 December 2014
Workshop details
| S. No. | TOPIC |
| 1. | Introduction |
|
|
| 2. | Methods of gait assessment  |
| 2.a | Techniques in 2D video analysis |
| Observational gait analysisFoot print method·Videographic/cinematographic analysis·Digital goniometric kinematic measurements | |
| 2.b | 3D Gait analysis |
|
|
| 3. | Gait deviations |
| Causes and factors affecting gait | |
| PT management of gait deviations | |
| Orthotic prescription | |
| 4. | Case Discussion |
Venue: – Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy Shivajinagar, Pune.
Contact hours – 16
Eligibility – Clinical Therapist, Post Graduate, 3rd & 4th year students and Intern
Registration fees: – Rs 2500 per candidate.
Limited Entries-30 only
Those who are interested please contact for registration.
Contact: – anjalipradhan.sha@gmail.com, gajanan_bhalerao@yahoo.com
ABOUT THE RESOURCE PERSON
Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT)
Associate Professor
Masters in physiotherapy, Neurosciences,
Certified Adult NDT (C/NDT) Therapist
Sancheti Institute College of physiotherapy,
HOD Physiotherapy Dept Sancheti Hospital
Shivajinagar, Pune.
gajanan_bhalerao@yahoo.com
Credits : University Topper in Master of Physiotherapy 2007 Pune university
Work Shops Conducted (Continued Medical Education)
- Workshop on Motor Relearning program for stroke
Rehabilitation at Youth Men Christian Association (YMCA), Pune, on 29th & 30th of March 2007.
- A 2 day workshop under Indian Association of Physiotherapy Pune branch, on “Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation” in 2008
- Resource person for the pre conference workshop and lecture during National Seminar On Multidisciplinary Approach To The Management Of Paediatric Disabilities organized by Faculty of Disability Management and Special Education Ramakrishna Mission Vivekananda University SRKV, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu 641 020, INDIA. June 2010
- A workshop on 2D & 3D Gait Analysis And Management Of Gait Deviations organized by Indian Association Of Physiotherapy Pune & Pimpri Chinchwad Branch on 27th &28th November 2010, at Sancheti institute college of physiotherapy.
- A workshop Motor Relearning program for stroke Rehabilitation on October 2010, organized by Indian Association of Physiotherapy Pune & Pimpri Chinchwad Branch on 27th &28thNovember 2010, at Sancheti Institute College of physiotherapy.
- A workshop on 2D & 3D Gait Analysis And Management Of Gait Deviations organized by Indian Association Of Physiotherapy Pune & Pimpri Chinchwad Branch on 27th &28th November 2010, at Sancheti institute college of physiotherapy.
- A workshop Spinal cord injury Rehabilitation, organized by Indian Association of Physiotherapy Pune & Pimpri Chinchwad Branch on December 2010, at Sancheti Institute College of physiotherapy.
- A workshop Spinal cord injury Rehabilitation, organized by Sancheti healthcare academy on December 2012, at Sancheti Institute College of physiotherapy.
- A 2 day Workshop on Task specific training in neuro rehabilitation, on 30 -31 sept 2013, at Mission health physiotherapy center Ahmadabad, Gujarat.
Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation : Workshops Details
Author of article:
DR. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT), PhD Scholor, MPTH NEURO, Certified Adult NDT therapist. HOD Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation Dept in Sancheti Hospital Shivajinagar Pune
Associate Professor & HOD PT in Neuro Rehabilitation DEPT at Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy, Shivajinagar Pune
We have to study all the Neuro therapeutic approaches in Neuro rehabilitation from BPT third year class, to fourth year and MPT. In these Approaches there are similarities and differences, advantages and limitations of each approaches need to be understood and studied during our graduation.
In third year and fourth year we need to discuss about it and show at least few techniques and do the demonstration on patients. It was very difficult for me to understand all these components and its was more difficult to apply these approaches in clinical practice.
Even though i was exposed to these approaches/technique it was very difficult to practice it. There was not enough opportunity to attend these kind of workshops or training. this thought process regarding this issue has been continuously thought-provoking in my mind. And i have experienced my students coming to me with the similar problem. they have been facing the similar problem like i use to.
There are so many approaches, What approach i suitable for my patient? This always a question with us all the time.
What is the technique i use for improving the desired control? The more try to answer this question we get more confused and we reach no where.
So i am planning to conduct a series of workshop on different approaches in neuro rehabilitation. These workshop will include practical demos on patients, clinical application of these approaches. These workshop will emphasis on similarities and differences, advantages and limitations approaches.
| Date | Topic | Participant Criterion | Participant fee INR | Resource | No. of days |
| 13/09/2014 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation :part I- Proprioceptive neuro Muscular facilitation.
https://gajananbhalerao.wordpress.com/2014/08/28/workshop-of%E2%80%8B-proprioceptive-neuro-muscular-facilitation-pnf-in-neuro-rehabilitation-on13th-sept-2014-%E2%80%8B/
|
4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 1000/-International US $25/- | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 1 DAY |
| 18th & 19th October 2014 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation : Part II- NDT /Bobath approach in Adult hemiplegia | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 2000/-International US $50/-/ | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 2 DAYS |
| 27th December 2014 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation : part III- Brainstorm & Roods approach | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 1000/-International US $25/- | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 1 DAY |
| 3rd & 4th January 2015 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation : part IV- Motor relearning program | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 2000/-International US $50/- | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 2 DAYS |
| 28th February 2015 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in neuro rehabilitation : part V- Recent advances with evidences.(CIMT, Mirror therapy, FES, BWSTT, mental imaginary training, strength training, robotic therapy etc) | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 1000/-International US $25/- |
Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT)
|
1 DAY |
Other Workshops
| November2014 | Spinal cord injury rehab | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 2000/-International US $50/-/ | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 2 DAY |
| 13th & 14th December2014 | 2D and 3D gait analysis and management of gait deviation | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 2000/-International US $50/- | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 2 DAYS |
| 14th & 15th March 2015 | Neuro therapeutic approaches in stroke rehabilitation: part VI- Motor control & Strategies to improve motor control | 4th year +, BPT, MPT30 students MAX | Indian –RS 2000/-International US $50/- | Dr. GAJANAN BHALERAO (PT) | 2 DAYS |
Please give your suggestions 
Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation workshop in Sancheti Institute college of Physiotherapy, Pune, August 2014
Sancheti institute College Of Physiotherapy organized a workshop on SPINAL-CORD INJURY REHABILITATION on 2nd August 2014 for final year BPTh students of Sancheti institute College Of Physiotherapy .
Course instructor was Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao (PT) MPTH Neuro, Associate professor, Sancheti College of Physiotherapy & HOD Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Sancheti Hospital, Pune.
Earlier We used to teach this in lecture format in regular class room teaching with didactic lecture. Last Few years we are doing in a workshop format where there get to learn the whole topic in 1 -2 days. This helps in continuity of lectures and practical demonstration, assessment and handling on patient.
In this course 42 students attended the work shop. The workshop included the neuro anatomy, mat exercises, transfer training, ambulation training etc. Participant were taught how to set the goals according to level, severity and available period of admission, OPD bases taking into account his lifestyle, contextual and environmental factors in his own home/village/town/city.
Practical demos of treatment on patients was shown. Different techniques of facilitation of control/strengthening was demonstrated on patients with incomplete cord injury TYPE B/C/D/E. Two quadriplegic who were showing type A in first few months were called in the workshop who are now high functioning walking independently. Indications and contraindication of different orthotics and prescription of orthosis taught .
Workshop details
| Saturday – 2nd August 2014 |
| Registration and breakfast |
Introduction
|
| Physical therapy evaluation and goal setting; ASIA scale |
| Functional goals & Strategies for functional rehabilitation |
| Case Studies |
| Evaluation |
| Treatment |
| Assessment, prescription & Wheel chair ambulation training |
| PWB Treadmill Training role of Central pattern generators(CPG) |
| Orthotic prescription |
| Stair case climbing training |
| Gait training. |
| Bladder and Bowel training |
| Bed sore prevention |
| Role Of Stem Cell Therapy |
Participant’s Feedback on course content and training was taken at the end of both day. All the students like the detailed anatomy and its clinical apllication, differential diagnosis & classfication of different spinal cord injury. Every learned a lot from the lab session of ASIA assessment on patients. On post workshop feedback all the participaants reported that, they leanred lot of new techniques of faciltation, multiple alterantive methods for bed mobility, transfers and ambulation training, wheechair modification, Orthotic fixation, and Role of steam cell in SCI rehabilitation. Everone extreamely satisfied.
STUDENTS FEEDBACK
PRIYAMWADA HINGE
THE SCI WORKSHOP WAS VERY HELPFUL.I learnt how to have a positive perspective about treatment of SCI patients by looking at what we can make them do rather than what they can’t do at the given time.
The actual practicals done on the patient were good
I learnt how to formulate goals for the patient and what my actual goal should be i.e. making my patient functionally independent as much as possible.
I also learnt the scales how I would document the case.
WORKSHOP ADVANTAGES
Is conducted at a stretch, so the continuity link is helpful.
We got to be in a different atmosphere ,we had a feeling that we are here to learn something different and important, so I think we were more attentive.
DISADVANTAGES
If it is for a long time, it becomes tiresome.
RUDRI PUROHIT
ADVANTAGES
We got to know about the details of SCI, their mechanism, evaluation, assessment and management.
Most important thing was that we got assess patients and actually see how difficult it is and it isn’t the same to practice on normal individuals.
Plus it is important that if you are teaching a para or a quadri transfers, then you as a therapist must know to do it very well.
WORKSHOPS attract better participation of students than lectures.
Clinical exposure was there and the experience was great.
We got to prioritize the treatment methods.
BAD POINTS
Instead of one day, we could split it into 2 days.
SHARWARI MUTSADDI
I LEARNT:
Depending on the segmental level, there is a certain functional level of independence which can be attained.
Different types of orthosis which can be used.
Mat exercises
-Transfers
-Walking
-Bed mobilizations
Driving rehab.
Goal setting in different conditions.
Wheelchair mobility.
Advantages
Stimulated us to think.
Showed us practically on patients.
PPT and pictures were good.
Workshop environment was good.
Disadvantages
Workshop was too long
JAYDEEP SAMANT
ADVANTAGES.
We got to know about ‘what can we do’; rather ‘what is to be done’.
The inclusion of actual patients helped getting a hands on of the techniques demonstrated.
DISADVANTAGES
We could have had skipped accessory discussions like vehicle modifications rather made that discussion shorter to give more time to other topics.
We hope we can have such a workshop again after a certain fixed time so as to apply techniques learnt in lectures in that timeframe.
DEEPALI SHETH.
ADVANTAGES
One of the best method of learning is practically on the patient and is very helpful for understanding.
DISADVANTAGES
Just one day is not enough to learn about SCI
Becomes a bit saturating if tried to fit in one day.
THINGS I LEARNT
Function oriented Rx planning.
Gave us a more practical thinking.
HARDI SHAH
ADVANTAGES
Understood very nicely on seeing it on the patient.
Management was taught well.
Practicals shown on wheelchair and mat were well understood.
Workshop teaching is very interesting because it concentrates on powerpoint as a theory part and on patient evaluation and management as a clinical part.
I learnt to classify SCI and understand level of injury.
How to manage the patients Rx and meet his/her functional goals was taught well.
It was an interactive workshop which made us think a lot and put forward our ideas and doubts.
I didn’t find any bad points. I have learnt a lot.
UNNAMED
ADVANTAGES
Workshop pattern was very interactive.
Interesting than classroom lectures.
Learning on patients was the best way.
I LEARNT.
Proper assessment in paraplegics.
Short and long term goal management.
NENCY MEHTA
Todays workshop was of great benefit to us. Many wrong concepts were cleared and the most important part was the practical examination on the patient. Every topic should be covered in this manner only.
The main doubt was planning management for quadriplegics, which got cleared, and also going about outcome measures, priority for each patients, how it differs and functional training is the utmost important final step was understood.
It was well understood. It was very innovative and very different from regular classrooms.
I had wrong concepts for how to judge the level of injury, which I understand after this workshop, and I will now be able to assess patients in a better way.
Thanks a lot sir, it was of great help.
Looking forward to the next workshop.
ABOLI AJGAONKAR
ADVANTAGES
Very helpful workshop and got to learn about transfers and modifications which can be done to aid the
Patient needs.
Practicals on patients was a good teaching method. Please have many more like these.
Mat exercises done on normal people don’t tell us about its complexities, so doing so on patients helped us correct our techniques.
DISADVANTAGES
It was hectic.
NAFISA MOTIWALA
ADVANTAGES
Effective as it was patient based.
Pictures and ppt were effective.
Was a very interactive session.
Learnt management in a better way
DISADVANTAGES
Was conducted for a long time.
SONAL GHUGARDARE
ADVANTAGES
Learning practically on the patients was helpful
No need to refer books for basic management.
DISADVANTAGES
Assessment should’ve been also taken in detail ( along with functional scales)
SAYALI KHEDEKAR
GOOD POINTS
Interactive sessions, make learning easy, as questions asked by others clear doubts.
Less monotonous.
Patients took part in our session and helped us imply our knowledge. Hence, made us learn applicability of physiotherapeutic techniques.
Good hands on.
Made clear of short term and long term goals in para and quadri patients
Mat exercises helpful.
Would help in Rx, assessment and planning in future and also on patient.
BAD POINTS
The session could have been more topic and time oriented but in all was a good experience.
CHETNA VARMA
ADVANTAGES
Workshop pattern helped us understand better.
A classroom lecture before the workshop helped us grasp better,
Management of Rx with help of patient helped retain things better.
Additional points with ppts helped clear the picture about orthosis,etc
Now, assessing SCI patients is easier.
Mat exercises are now more thorough.
DISADVANTAGES
Time management was bad.
UNNAMED
GOOD POINTS
The workshop was very interesting and practical demos were helpful.
Was not boring due to interactions and my neuro doubts were cleared.
BAD POINTS
Was too long, I feel multiple shorter sessions would serve the purpose.
ABHISHEK GUJAR
Injury levels were explained and on patient demos were very good.
Very good demos on wheelchair transfers.
Different types of transfers well shown.
Self practice made us understand better.
KHUSHBOO TAHILRAM
GOOD POINTS
Workshop pattern is very good.
Environment change helps in learning.
Teaching method to include practical examples of patients helped us see approaches and problems. Was not ABSTRACT.
BAD
Was a little too stretched, by the end of the day, saturation.
WHAT I LEARNT
Practical ways to handle a patient
Handling skills
Open minded approach to Rx
Goal setting as per patient needs
Activity oriented goal setting
Positive attitude of therapist to goal outcomes
SUPRIYA DHADDHA
The workshop was more practical and management orientedwith hands on, on the patient
Practical knowledge on how to plan Rx of patient in relation to his or her need and not just focus on the objective management like ROM and strength training.
The ppt and viedos helped us understand more about actual patients and how they do ADLs even after this trauma
Various modes of management were taught in a patient and also setting Long and Short term goals was taught nicely.
Workshop training is more interesting and we pay more attention in it.
RUCHA DESHPANDE
GOOD POINTS
One of the best method to learn, practical on patients helps us understand better
Better than classroom lectures.
Practically used methods were focused upon rather than textbook methods
BAD POINTS
One day isn’t enough to learn about SCI. It becomes saturating and hectic.
THINGS I LEARNT
Function oriented Rx planning.
Practical thinking.
DIVYA DESAI
GOOD POINTS
Interactive and interesting.
The practical demonstrations on the patients and wheelchair demonstrations helped us learn better.
Understanding how to treat a SCI patient on the basis of patient’s current disabilities helped us learn better rather than learning it in a classroom by imagining a case.
Planning management of SCI patients is easier as we know what lies in short and long term goals.
More such sessions should be held.
ANAY DESAI
Sir, it was a marvelous experience.
I understood the Rx part which is more important than the theory part.
On patient eval and Rx was a good idea.
GOOD POINTS
Very good idea to change the place as classrooms give a monotonous feel.
Demos were helpful
Very well managed by sir and coordinators. No time wasted
BAD POINTS
I feel 9 to 5.30 is too much CNS on CNS load.
KINJAL SANGANI
GOOD POINTS
On patient skills.
Proper clinical exposure
To plan Rx as per patients activity and participation.
Don’t actually work on impairment.
Workshop is way better than classroom teaching or seminars.
Got to know assessment and using ASIA scale
Transfers, pre ambulatory training was helpful.
How to reduce therapist load with proper use of biomechanics.
How to give commands.
BAD POINTS
It is difficult to transfer patients in case therapist strength is less.
What should be the modification in relation to this?
MAYURI CHAUDHARI
GOOD POINTS
Explanation with a lot of examples.
On patient demos.
Management protocols
95% understanding
Proper understanding of wheelchair ambulation and transfer.
ASIA scale description
Change of environment helped understanding
Explanation of each goal
WHAT I LEARNT
I understood it better on the patient and also the wheelchair transfers and ambulation.
KRUPA DOSHI
The workshop was very effective, way better than classroom lectures.
Was effective as we learnt to assess the level of injury by myotomes and also what to expect from the patient.
We learnt that functional activities are more important than strengthening.
We learnt to look at the bigger picture rather than focusing on individual impairments.
BAD POINTS
It would be better if we got more patients and more groups so all of us could practice.
In the end, if you would have had given us a simulated case for us to assess and plan the Rx on a model it would’ve been better.
KALYANI SHIVARKAR
GOOD POINTS
Workshop format helped understand SCI better.
Theory and practical were both covered well
Functional independence, activity and participation should be the goals of Rx, I will never forget that
Learnt a lot of transfer methods.
Overall, workshop teaching was way better than classroom teaching.
GEETARANI MATURI
Patient management was taught very well
Education about orthosis and prosthesis was helpful
Theory was minimum
Learnt well about patient Rx,evaluation, handling and transfers very well
Workshop pattern was better than classroom pattern.
BAD POINT
Did not understand lecture towards the end as it was saturating.
WAGEESHWARI MADGULKAR
GOOD POINTS.
Really helpful workshop
Practical format helped understand better
Transfer methods and rehab part were taught well
Unclear concepts were cleared.
BAD POINTS
Many things were taught in a short time, so towards the end, it was less understood.
WHAT I LEARNT:
Methods of transfer and patient handling
Stepwise and easy rehab management of SCI patients.
RUJUTA RAUT
GOOD POINTS
Was a good learning experience and a good amount of demos were included.
Live practical on patient demos helped understand various problems faced while actually treating.
All doubts adequately cleared.
Was a better environment than a classroom
WHAT I LEARNT:
My doubts about orthotics were classified to great extent.
Goal setting was well classified.
Patient eval will now be easier
Learnt importance of patient interaction and proper commands
SAANIA KASLIWAL
GOOD POINTS
We liked the way it was conducted
Practical demos was the best part.
Many doubts were solved
Now we can go about with the management of SCI patients.
It will be really helpful for our future.
BAD POINTS
Time duration was very long
WHAT I LEARNT:
Management of SCI patients
Handling skills
Orthotics was taught
Wheelchair transfers were shown.
PRIYA GOGRI
GOOD POINTS
Workshops are a better way of teaching and I was more attentive throughout the workshop than I would be in the class and grasped very well.
We could practically see on patients and imply our learning directly on them.
Doubt solving played a great role in understanding the topic.
BAD POINTS
The workshop duration was a little too much, as in the end, it was a bit too over my head and couldn’t concentrate well in the end.
MEENAKSHI KADAM
ADVANTAGES
On patient learning is the best way of learning.
Hands on was better than classroom lectures.
Two way interactions were better than classroom lectures.
Change of environment.
DISADVANTAGES
Time limitation is a major setback.
WHAT I LEARNT:
80% of SCI doubts cleared.
Learning and interaction abilities improved
My goal of treating disabilities turned into making the patient independent.
NDTA Advanced Handling and Problem Solving Course Pune, Maharashtra, India 2015
NDTA Advanced Handling and Problem Solving Course
Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy, Pune, Maharashtra, India
Course Description
This five-day course is designed to broaden one’s knowledge base and enhance skills learned in the certificate course. An emphasis will be placed on enhancing participants’ assessment and handling skills. The patient practicum of the course will involve patients with a variety of acquired CNS lesions (stroke, traumatic brain injury, and ataxia if possible). The registration form asks you to state specific questions you would like addressed during the course. As much as possible, we will try to address your clinical questions. Participants must have completed an NDT/Bobath Certificate Course in the Treatment and Management of Adults with Hemiplegia or a Certificate Course in the Treatment and Management of Individuals with Cerebral Palsy as a prerequisite to this course.
Course content will include:
- ICF Enablement Model (from the WHO) for assessment and intervention planning
- Current concepts of postural control and movement
- Analysis of complex movement patterns related to function
- Analysis of atypical movement patterns
- Problem-solving and Intervention principles and strategies
Course will include lab, lecture and patient demonstrations. Participants will treat patients at least four of the five days of this course.
Course Objectives
Upon completion of the course, the participant will be able to:
- Utilize the ICF Enablement Model for patient evaluation and intervention planning
- Identify current concepts of postural control and movement
- Analyze factors which interfere with the performance of functional activities
- Identify impairments contributing to these ineffective posture and movement strategies
- Synthesize information to develop appropriate intervention strategies for persons with neurological dysfunction
- Demonstrate ability to implement appropriate intervention strategies during treatment practicum
Course Dates:
- 01-12-2015 – 01-16-2015
Course Number: 15H101
Course Status: Approved
Prerequisite: NDT/Bobath Certificate Course
Location: Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy
Sancheti Health Academy, Shivajinagar, Thube Park 11/12
Pune, Maharashtra, India, 41105
Course Instructors:
Cathy Hazzard, B.Sc, MBA, PT, C/NDT CI
Course Contact:
Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao
Phone: 9198 22623701
Fax: 9120 25539494
gajanan_bhalerao@yahoo.com
Advance NDT course
Registration Fee: A non-refundable RS 3000/- and $ 50 for international delegates (No application will be processed without it).
Course Fees: These include course tuition fees, course material, daily breakfast, lunch and high tea on all 5 days of course (5day/week).
|
TYPE
|
PERIOD
|
INDIAN DELEGATE
|
INTERNATIONAL DELEGATES.
|
|
Registration Fee
|
Up to 31/09/14
|
Rs 3000/-
|
$ 50
|
|
Early bird Fee
|
Up to 30/09/2014
|
Rs 35,000/-
|
US $ 650/-
|
|
Regular Fee
|
01/10/2014 TO 31/10/2014
|
Rs 40,000/-
|
US $ 700/-
|
|
Late Fee
|
01/11/2014 TO 30/11/2014
|
Rs 45,000/-
|
US $ 750/-
|
After November 31st registration is closed.
Please register early to get benefit.
Please Send DD/ Multi city Cheque in favor of “Sancheti Continuous Physiotherapy Education (CPE) Program” payable at Pune.
Please click here for application
advance course Application for NDTA Adult Certificate course 2015 India –
NDT/Bobath Certificate Course in the Management and Treatment of Adults with Hemiplegia, Pune, India 2015
NDT/Bobath Certificate Course in the Management and Treatment of Adults with Hemiplegia
Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy, Sancheti Health Academy, Shivajinagar, Pune, Maharashtra, India
Sancheti is organising second ADULT NDT course in INDIA.
Seats available – 24 only
Course Dates:
19-01-2015 – 06-02-2015
It will be 5 days/week for three weeks. Saturday & Sunday off.
Course Number: 14A101
Course Status: Approved
Registration Fee: A non-refundable RS 5000/- and $ 100 for international delegates (No application will be processed without it).
Course Fees: These include course tuition fees, course material, daily breakfast, lunch and high tea on all 15 days of course (5day/week).
| TYPE | PERIOD | INDIAN DELEGATE | INTERNATIONAL DELEGATES. |
| Registration Fee | Up to 31/09/14 | RS 5000/- | $ 100 |
| Early bird Fee | UPTO 30/09/2014 | Rs1,00,000/- | US $ 2050/- |
| Regular Fee | 01/10/2014 TO 31/010/2014 | Rs1,10,000/- | US $ 2100/- |
| Late Fee | 01/11/2014 TO 31/30/2014 | Rs1,20,000/- | US $ 2150/- |
After November 31st registration is closed.
Please register early to get benefit.
Please Send DD/ Multi city Cheque in favor of “Sancheti Continuous Physiotherapy Education (CPE) Program” payable at Pune.
Banking details for electronic transaction
Bank name: Bank of Maharashtra
Branch: Pune Main branch, Lokmangal Pune -411005
IFSC code: MAHB0001150
Account name: Sancheti continuous physiotherapy education (CPE) program
Account number: 60130671451
Note: We reserve the right to cancel this course, if necessary. Full tuition reimbursement will be provided on a prorated basis in the event of sponsor or Coordinator-Instructor cancellation.
(NOTE: Application fee is non-refundable.)
Location: Sancheti Institute College of Physiotherapy, Sancheti Health Academy
Thube Park 11/12
Shivajinagar, Pune, Maharashtra, India, 41105
Faculty
Cathy Hazzard, B.Sc, MBA, PT, C/NDT CI
Ms. Katy Kerris, OT, C/NDT
Course ID no. 15A101
Cathy Hazzard, B. Sc. P.T., MBA is a Physiotherapist with over 25 years experience working with adults with varied neurological diagnoses. Her clinical background also includes experience and continuing education courses in manual therapy and orthopedics. She obtained an MBA in 1993 while continuing to work as a PT. She has been an NDTA™ Coordinator Instructor in Adult Hemiplegia since 1998 and has taught introductory, certificate and advanced level NDT courses extensively throughout North America (Canada, United States, and Mexico) and internationally in such countries as Ireland, Hong Kong, Singapore, Estonia, Colombia, and Peru. Cathy practiced in Calgary, Alberta, Canada for over 20 years in the acute, rehabilitation and outpatient phases of care. She is now working in private practice and Home Health on Vancouver Island, British Columbia. Cathy served as the Chair of the NDTA™’s Instructor Group from 2002 – 2005 and a member of the Board of Directors of NDTA™ from 2003 – 2007. (http://www.ndta.org/instructor_detail.php?instructor=768)
Ms. Katy Kerris, OT, C/NDT
She has 25 years of experience working with neurologically impaired and orthopedic patients. She uses an NDT perspective in treating neuro patients. In addition she has a Certified Hand Therapist and also have a strong background in manual therapy.she is an OT Adult Hemi Instructor. She has taught several introductory level classes and assisted in teaching several 3 week certificate courses.
Course Contact:
Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao
Phone: 9198 22623701
Fax: 9120 25539494
gajanan_bhalerao@yahoo.com
Website
http://www.ndta.org/course_list.php?type=AH
Application of Registration:-
Hydrotherapy for traumatic brain injury with hemiplegia – our challenges and solutions

This is the case of a 16 yr old boy who met with an accident leading to a traumatic head injury in August 2011. He was in a coma for 1 month after which he gradually started showing improvement. I started treating him in January 2011. He had suffered a diffuse axonal injury due to which both the sides of his body were involved. Initially he was hypotonic on both sides and trunk . He could move his left side voluntary control grade III in upper and lower limb but no control on right side. Within next 2 months he started sitting without support, supine to sit with support and required minimum to moderate assistance for sit to stand from high bed. He could stand with weight bearing on both legs with moderate assistance. His left side improved up to grade VI. His tone in trunk & RT upper & lower limb started improving (grade II).
Assisted walking training on the ground
In March and April 2012 he was showing a picture of RT hemiplegia with grade II in UL & LL with developing spasticity. We used to make him walk with FRO and push knee brace on Rt (hemiplegic side). Initially with back forearm support walker then without walker. Assisted walking training was started ( we have to passively step forward the hemiplegic leg ).
He could move the limb in supine but could not take a step forward while walking on ground. So we have decided to take him for hydrotherapy to improve his control of lower limb and active walking. Taking a Patient to hydrotherapy was a good idea but we do not have hydrotherapy centre/ swimming pool for patients in Pune (Except in Aditya Birla hospital). So we contacted one of the commercial pool in Kalyaninagar. We explained them the condition of the patient & our objective. Then they gave us the permission. They have given us two lifeguards to help us during training session in the pool.
We were alloted a time of 7 pm to 8pm as the pool was occupied at other times. So, the patients had to adjust accordingly as they were not allowed to come along with regular batches.
Getting in Pool (Transfer)
While going for swimming we had one more challenge of how to take the patient in the pool (transfer)? So for that I used my Ganpati Transfer method. We made the patient to sit on the thick towel, the towel acted like a sling where the patient was sitting in the centre of the sling. Then two people were holding the towel from the sides, this helped to lift the patient easily. After lifting the patient we made him sit at the edge of the swimming pool with his legs dangling in the pool. Then he was assisted to slide down in the pool so that he can stand in the pool. This was a very easy and safe transfer.
Because patient had a poor balance he could not stand in the pool and poor control of Rt (hemiplegic side) he could not swim independently. So we made him lie-down on the Raft with his trunk on the raft. Which helped to control weight of the body and arms & legs were free to move.
 As he was able to move the normal upper and lower limb he started to stroking/swing them in the water which helped him to propel his body forward in water. We were assisting the hemiplegic upper and lower limb for stroking/swinging.
As he was able to move the normal upper and lower limb he started to stroking/swing them in the water which helped him to propel his body forward in water. We were assisting the hemiplegic upper and lower limb for stroking/swinging.
This is how we started swimming a patient with head injury with Hemiplegia in the water with help of Raft. We continued this Practice daily evening for about two months (6days/week)
Assisted Walking Training in Water
He was having lot of difficulty in walking steeping forward on ground, while doing assisted walking with AFO and Long knee Brace on Hemiplegic side. so we started training of assisted walking in water, with hand support. Because of the bouyancy his body weigth was reduced and he could stand in water with minimum assistance, this also helped in stepping forward the hemiplegic leg. It was very easy for him to walk in water with less support.
We were Training him Assisted Walking on ground since 2 months but he could not step forward actively, but after training of walking in water for 1 months he could step forward on ground also with walker without assistance.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh0Cvh1O-O4
Related articles
- Traumatic Brain Injury Infographic Released – Shulman DuBois LLC Reviews the Basics of TBI Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment (prweb.com)
- How a single brain trauma may lead to Alzheimer’s disease(sciencedaily.com)
- The Benefits of Swimming (veganurbanite.com)
- Water Exercise Boosts Endurance in COPD (nlm.nih.gov)
Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation workshop organized by Indian Association of Physiotherapist Pune Branch and Sancheti Institute college of Physiotherapy, Pune
Indian Association Of Physiotherapy Pune Branch & Sancheti institute College Of Physiotherapy organized a workshop on SPINAL-CORD INJURY REHABILITATION on 27th and 28st October 2012 . Course instructor was Dr. Gajanan Bhalerao (PT) MPTH Neuro, Associate professor, Sancheti College of Physiotherapy & Inchargeof Department of Neuro and Spine Rehabilitation Sancheti Hospital, Pune.
In this course 32 students from all over Maharashtra Physiotherapy colleges & clinical therapist attended the work shop. The workshop was inaugurated By Dr. Meenakshi Pandit, Convener IAP Pune branch, along with Dr. Apurv Shimpi Treasure Executive Committee Member Dr. Anushree Phansalkar IAP Pune branch.
We had Invited Major Bist, administrator director Paraplegic R ehabilitation Centre Kharaki, Pune to give information the functioning and activities of paraplegic at their centre. Pararaplegic are living at the centre and all of them are independent in their lifestyle and earning livelihood through vocational rehab.
ehabilitation Centre Kharaki, Pune to give information the functioning and activities of paraplegic at their centre. Pararaplegic are living at the centre and all of them are independent in their lifestyle and earning livelihood through vocational rehab.
Dr. Vijay Gupta MPT neuro (USA) was also helped during the practical session for supervising the particiapnt practice of practical demos done in the workshop.
The workshop included the neuro anatomy, mat exercises, transfer training, ambulation training etc. Participant were taught how to set the goals according to level, severity and available period of admission, OPD bases taking into account his lifestyle, contextual and environmental factors in his own home/village/town/city.
Practical demos of treatment on patients was shown. Different techniques of facilitation voluntary control/strengthening was demonstrated on patients with incomplete cord injury TYPE B/C/D/E. Two quadriplegic who were showing type A in first few months were called in the workshop who are now high functioning walking independently, driving two wheelers with added two wheels independently . Car transfers’ training of patients was shown. Indications and contraindication of different orthotics and prescription of orthosis taught .
Modified bike for para
car transfers 
Car modifications
Workshop details
| Day 1 Saturday -27th /10/12 |
| Registration and breakfast |
Introduction
|
| Physical therapy evaluation and goal setting; ASIA scale |
| Functional goals & Strategies for functional rehabilitation |
| Case Studies |
| Evaluation |
| Day two Sunday – 28th/10/12 |
| Assessment, prescription & Wheel chair ambulation training |
| PWB Treadmill Training role of Central pattern generators(CPG) |
| Orthotic prescription |
| Stair case climbing training |
| Gait training. |
| Bladder and Bowel training |
| Bed sore prevention |
| Role Of Stem Cell Therapy |
Participant’s Feedback on course content and training was taken at the end of both day. All the students like the detailed anatomy and its clinical apllication, differential diagnosis & classfication of different spinal cord injury. Every learned a lot from the lab session of ASIA assessment on patients. On post workshop feedback all the participaants reported that, they leanred lot of new techniques of faciltation, multiple alterantive methods for bed mobility, transfers and ambulation training, wheechair modification, Orthotic fixation, and Role of steam cell in SCI rehabilitation. Everone extreamely satisfied.
STUDENTS PARTICIPATED IN WORKSHOP
| S. NO. | NAME | STATUS | PLACE |
| 1 | RADHA AJAY MEHTA | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 2 | NEHA MANJUNATH | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 3 | JUIE MESVANI | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 4 | HETAL JITENDRA SHAH | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 5 | HIRAL PRASHANY SAMPAT | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 6 | DEEPMALA DINESH SHARMA | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 7 | DARSHINI VIJAY DESAI | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 8 | SNEHA JADHAV | INTERN | PUNE |
| 9 | MANALI DEVANE | MPT | PUNE |
| 10 | RUCHITA KOTEWAR | MPT | PUNE |
| 11 | SURYAKANT GADGERAO | MPT | PUNE |
| 12 | TUSHAR DHAWALE | MPT | PUNE |
| 13 | MRUNAL HARLE | MPT | PUNE |
| 14 | PRATIBHA SALKAR | MPT | PUNE |
| 15 | ARCHANA GIDWANI | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 16 | SADHANA | MPT | PUNE |
| 17 | PURTI | MPT | PUNE |
| 18 | RASHMI | MPT | PUNE |
| 19 | NIMISHA MISHRA | MPT | PUNE |
| 20 | SANNA SAYED | PRACTICE | MUMBAI |
| 21 | SHARDA BHALERAO | INTERN | PUNE |
| 22 | CHETANA AHER | INTERN | PUNE |
| 23 | JAY PAWAR | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 24 | ABHA BHUTADA | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 25 | RAJASHREE FADNAVIS | MPT | PUNE |
| 26 | APOORVA PHADKE | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 27 | ASHWINI KAMBLE | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 28 | NITIN CHOUKE | MPT | PUNE |
| 29 | CHANDALI DOSHI | MPT | PUNE |
| 30 | HARSHIKA BHANUSHALI | INTERN | PUNE |
| 31 | SNEHA MULE | PRACTICE | PUNE |
| 32 | DENZIL FERNANDES | PRACTICE | PUNE |















































































































































You must be logged in to post a comment.